
- decrease across a period with increase in number of valence electrons as well as a decrease in atomic radius
- increase down the group with increase in number of shells and atomic radius
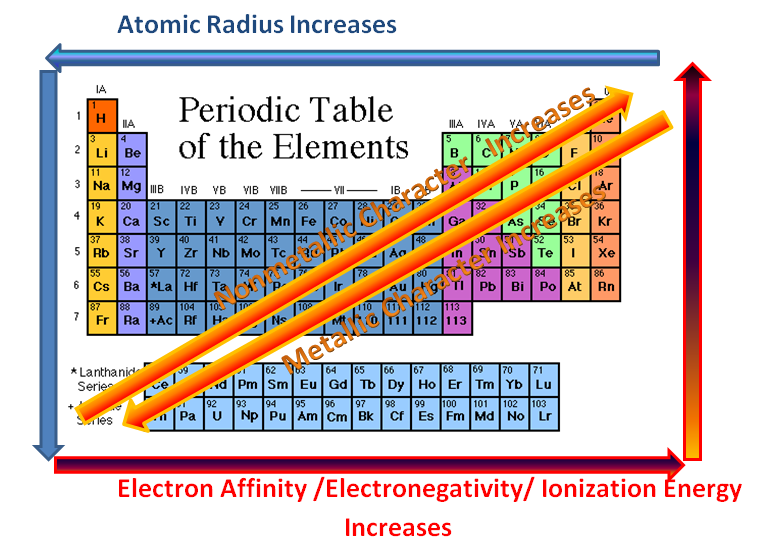
- the distance from the atomic nucleus to the outermost stable electron orbital in an atom
- decrease as one progresses across a period from left to right because the effective nuclear charge increases, thereby attracting the orbiting electrons and lessening the radius
- usually increases while going down a group due to the addition of a new energy level (shell)

- minimum amount of energy required to remove one electron from each atom in a mole of atoms in the gaseous state
- increase while one progresses across a period because the greater number of protons (higher nuclear charge) attract the orbiting electrons more strongly
- As one progresses down a group on the periodic table, the ionization energy will likely decrease since the valence electrons are farther away from the nucleus and experience a weaker attraction to the nucleus

- a measure of the ability of an atom or molecule to attract pairs of electrons in the context of a chemical bond
- as one moves from left to right across a period in the periodic table, the electronegativity increases due to the stronger attraction that the atoms obtain as the nuclear charge increases
- Moving down a group, the electronegativity decreases due to the longer distance between the nucleus and the valence electron shell, thereby decreasing the attraction, making the atom have less of an attraction for electrons or protons
- how likely or vigorously an atom is to react with other substances
- Metals Period - reactivity decreases as you go from left to right across a period
- Non-metals
Group
- reactivity increases as you go down a group
- Period - reactivity increases as you go
from the left to the right across a period
- Group - reactivity decreases as you go down the group

Melting Point and Boiling Point
- Metals - the melting point for metals generally decreases as you go down a group.
- Non-metals - the melting point for non-metals generally increases as you go down a group.
No comments:
Post a Comment